
A lighter engine means the whole car weighs less and is more efficient. Naturally-aspirated diesel engines, by contrast, produce a lot of torque at low revs. Adding a turbo amplifies the effect which is why turbo diesels feel so strong if you floor the throttle at, say, 50mph in top gear.
Turbocharged cars also have quieter exhaust pipes. This is simply a function of the time it takes for the exhaust gases to reach the turbo and spin the turbine up to speed. A big turbo often exaggerates the effect, as large turbine blades take longer to get up to speed.
Modern turbos have many ways of reducing lag. Some engines have two more turbos of increasing size that operate at different revs, while car makers have also developed electric motors that spin the turbine before gases even reach it.
Turbos are another thing to go wrong, as well. They can and do — some engines are particularly prone to turbo issues.
Thick, white exhaust smoke and a loss of power are the clues. Superchargers also boost power by forcing more air into the engine, but the turbine is spun by the engine itself. Yes, broadly speaking — although not in name.
Porsche is using the Turbo moniker to denote the most powerful versions of its Taycan EV , while there is also the possibility that future engines could burn hydrogen, and utilise turbos to help with this.
Looking for an easy way to change your car? Then carwow is the place to go. You can sell your old car for a great price, and get the best deals on a new one. All through our network of trusted dealers and all from the comfort of your home.
Tap the button below to get started today. Sell your car today Dealers bid to buy your car! Home New Used Sell Sell Electric Leasing Reviews SALE. What is a turbo and what does it do? Next step is to determine how much pressure loss exists between the compressor and the manifold.
The best way to do this is to measure the pressure drop with a data acquisition system, but many times that is not practical. For our examples we will estimate that there is a 2 psi loss. Therefore we will need to add 2 psi to the manifold pressure in order to determine the Compressor Discharge Pressure P 2c.
To get the correct inlet condition, it is now necessary to estimate the air filter or other restrictions. In the Pressure Ratio discussion earlier we said that a typical value might be 1 psi, so that is what will be used in this calculation.
Also, we are going to assume that we are at sea level, so we are going to use an ambient pressure of We will need to subtract the 1 psi pressure loss from the ambient pressure to determine the Compressor Inlet Pressure P1.
With this, we can calculate Pressure Ratio using the equation. For the 2. We now have enough information to plot these operating points on the compressor map. First we will try a GTR.
This turbo has an 88mm tip diameter 52 trim compressor wheel with a As you can see, this point falls nicely on the map with some additional room for increased boost and mass flow if the horsepower target climbs.
For this reason, the GT37R turbo family is applied on many of the Garrett Powermax turbo kits that are sized for this horsepower range. This category is for daily driven vehicles that have up to horsepower over stock or wheel horsepower. Looking at the previous map, the compressor does not flow enough to support this requirement, so we must look at the next larger size compressor.
Another option that could also be considered is the GTR which has a slightly larger inducer compressor and the next larger frame size turbine wheel. This category is for real hot rod vehicles that have up to horsepower over stock and owners that are willing to give up some of the daily utility in order to achieve higher power gains.
For this flow and pressure ratio, the GTR is appropriate and is shown below. Since this is approaching a pressure ratio of 4-to-1, we are about at the limit of a single turbo on an engine of this size. The final case is the Competition category.
Since this is a special case and there are so many ways to go about an ultimate power diesel application, it is not possible to cover it adequately in this article. There are, however, some general guidelines. At this power level, as stated above, it is a good idea to consider a series turbo application.
This is a situation where one turbo feeds another turbo, sharing the work of compressing the air across both compressors. The low-pressure compressor feeds the high-pressure compressor which then feeds the intake. On the turbine-side the exhaust first passes through the high-pressure turbine and then on to the low-pressure turbine before being routed out through the tailpipe.
We can still calculate the required mass flow, but the pressure ratio is more involved and questions should be discussed with your local Garrett Powermax distributor. To calculate the required mass flow, we use the normal equation.
This time the power target will be wheel horsepower over stock, for a total of wheel horsepower. This air flow rate will apply only to the low-pressure compressor as the high-pressure compressor will be smaller because it is further pressurizing already compressed air.
In most cases, the high-pressure turbo tends to be about two frame sizes smaller than the low pressure stage. So in this case, after selecting the appropriate low-pressure turbo hint: look at the GTR compressor map , a GTR or GTR would be the likely candidates.
Generally speaking, the proper turbine housing is the largest one that will give acceptable boost response on the low end while allowing for more optimal top end performance. This information should be used as a starting point for making decisions on proper turbo sizing.
Of course, for more specific information on your engine, consult a Garrett Powermax distributor. Sign up to receive exclusive communications about offerings, events and news, surveys, special offers, and related topics via telephone, email, and other forms of electronic communication e.
If you are a current customer, you will not be unsubscribed from transactional and other non-marketing communications, such as communications containing important information related to a product or service you have purchased.
If you would like to unsubscribe from all marketing communications from Garrett Motion Inc. and its affiliates and subsidiaries, click here. and its affiliates and subsidiaries. We apologise but this page is not available in your selected language,.
Please go back and choose a different language to view the content. We apologise for the inconvenience. Your personal data will be used to support your experience throughout this website, to manage access to your account, and for other purposes described in our privacy policy.
Please check here if you wish to receive future communications from Garrett, including notices of product updates or other promotional or technical information. We use this information in strict accordance with our Privacy Statement. By signing up, you are providing consent for Garrett Advancing Motion, Inc.
and its affiliates and subsidiaries to contact you through e-communications, which refers to email, social media and digital advertising. You can withdraw your consent at any time here. Choosing the right Turbo Choosing a performance turbocharger starts with a horsepower target.
Performance Upgrade. Boost Adviser Garrett Boost Adviser is a tool developed to perform a turbo match quickly and easily. Here, we list the main plus points of a turbocharged engine. Turbos produce more power in the same sized engine.
This means that more cars are now fitted with smaller, turbocharged engines, replacing larger and less economical units. Because turbochargers can produce the same power output as larger, naturally-aspirated engines, this paves the way for the use of smaller, lighter and more economical engines.
Now, all modern diesel cars are fitted with a turbocharger, improving fuel economy and reducing emissions. Even on the smallest engines, turbochargers produce more torque, particularly lower down the rev range.
This means cars benefit from strong, nippy performance, which is great around town and helps the engine to feel more refined at higher speeds on motorways and A roads. At low speeds, small turbocharged engines can outpace cars fitted with larger, naturally-aspirated engines, because of the torque they produce.
As the air in a turbocharged engine is filtered through more pipes and components, the intake and exhaust noise is reduced and refined, making for a quieter and smoother engine noise — perhaps one of the most unexpected benefits of a turbocharged engine.
Turbochargers add complexity to an engine, with a whole host of other components beneath the bonnet that can fail or develop faults.
These problems can be expensive to put right, and can have an impact on other components if they fail. This only really happens when the car is being driven aggressively, or from a closed throttle position. In high-performance cars, manufacturers prevent turbo lag by adding two turbochargers of differing geometry, rather than one big one with only a single turbine.
Drivers going from a naturally-aspirated car to a turbocharged model may need to adjust their driving style to maintain good efficiency, particularly when first setting off.
A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While
Video
I RACED A SLEEPER BIG TURBO G37! - Single Turbo G37 vs Single Turbo G37!Motor turbo - A turbocharger gives an engine extra power without sacrificing fuel efficiency. It is typically added to smaller engines to improve performance A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While
By altering the geometry of the turbine housing as the engine accelerates, the turbo's aspect ratio can be maintained at its optimum. Because of this, variable-geometry turbochargers often have reduced lag, a lower boost threshold, and greater efficiency at higher engine speeds.
An electrically-assisted turbocharger combines a traditional exhaust-powered turbine with an electric motor, in order to reduce turbo lag. This differs from an electric supercharger , which solely uses an electric motor to power the compressor.
The compressor draws in outside air through the engine's intake system, pressurises it, then feeds it into the combustion chambers via the inlet manifold.
The compressor section of the turbocharger consists of an impeller, a diffuser and a volute housing. The operating characteristics of a compressor is described by the compressor map. Some turbochargers use a "ported shroud", whereby a ring of holes or circular grooves allows air to bleed around the compressor blades.
Ported shroud designs can have greater resistance to compressor surge and can improve the efficiency of the compressor wheel. The center hub rotating assembly CHRA houses the shaft that connects the turbine to the compressor. A lighter shaft can help reduce turbo lag.
Some CHRAs are water-cooled and have pipes for the engine's coolant to flow through. One reason for water cooling is to protect the turbocharger's lubricating oil from overheating. The simplest type of turbocharger is the free floating turbocharger. Turbo lag refers to delay — when the engine rpm is within the turbocharger's operating range — that occurs between pressing the throttle and the turbocharger spooling up to provide boost pressure.
Methods to reduce turbo lag include: [ citation needed ]. A similar phenomenon that is often mistaken for turbo lag is the boost threshold.
This is where the engine speed rpm is currently below the operating range of the turbocharger system, therefore the engine is unable to produce significant boost.
At low rpm, the exhaust gas flow rate is unable to spin the turbine sufficiently. The boost threshold causes delays in the power delivery at low rpm since the unboosted engine must accelerate the vehicle to increase the rpm above the boost threshold , while turbo lag causes delay in the power delivery at higher rpm.
The most common arrangement is twin turbochargers, however triple-turbo or quad-turbo arrangements have been occasionally used in production cars.
The key difference between a turbocharger and a supercharger is that a supercharger is mechanically driven by the engine often through a belt connected to the crankshaft whereas a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the engine's exhaust gas. Supercharged engines are common in applications where throttle response is a key concern, and supercharged engines are less likely to heat soak the intake air.
A combination of an exhaust-driven turbocharger and an engine-driven supercharger can mitigate the weaknesses of both. are Garrett Motion formerly Honeywell , BorgWarner and Mitsubishi Turbocharger.
Turbocharger failures and resultant high exhaust temperatures are among the causes of car fires. Failure of the seals will cause oil to leak into the cylinders causing blue-gray smoke. In diesel engines, this can cause an overspeed, a condition known as diesel engine runaway.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Exhaust-powered forced-induction device for engines. Several terms redirect here. For other uses, see Turbo disambiguation. Cutaway view showing the two scrolls of a Mitsubishi twin-scroll the larger scroll is illuminated in red.
Main article: Variable-geometry turbocharger. This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
June Learn how and when to remove this template message. Main article: Twin-turbo. Main article: Supercharger Supercharging versus turbocharging. Main article: Twincharger.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Turbochargers. Retrieved 1 June Stuttgart: Robert Bosch. ISBN Retrieved 6 June Retrieved 3 August Encyclopedia of the History of Technology. London: Routledge. Archived from the original on 13 July Retrieved 30 June Retrieved 22 July Retrieved 20 September Porsche Turbo: The Full History.
MotorBooks International. Turbo: Real World High-Performance Turbocharger Systems. CarTech Inc. Archived from the original on 5 April Retrieved 2 August Birkhäuser Verlag. Archived from the original on 29 September Theodore Gresh. Archived from the original on 4 March Retrieved 15 April This air mixes with the injected fuel allowing the fuel to burn more efficiently so increasing the power output of the engine.
One other side of turbocharging, which may be of interest, is an engine which works regularly at high altitudes, where the air is less dense and where turbocharging can restore some of the lost power caused by the drop in air pressure.
Instead of escaping through the exhaust pipe, hot gases produced during combustion flow to the turbocharger. The cylinders inside an internal combustion engine fire in sequence not all at once , so exhaust exits the combustion chamber in irregular pulses.
Conventional single-scroll turbochargers route those irregular pulses of exhaust into the turbine in a way that causes them to collide and interfere with one another, reducing the strength of the flow.
In contrast, a twin-scroll turbocharger gathers exhaust from pairs of cylinders in alternating sequence. The exhaust strikes the turbine blades, spinning them at up to , rpm. The alternating pulses of exhaust help eliminate turbo lag.
Having served their purpose, exhaust gases flow through an outlet to the catalytic converter, where they are scrubbed of carbon monoxide, nitrous oxides and other pollutants before exiting through the tailpipe. Dense, oxygen-rich air flows to the combustion chamber. The additional oxygen makes it possible for the engine to burn gasoline more completely, generating more performance from a smaller engine.
Any Questions? Call us on or simply click on one of the buttons below. Basket 0. Item added to order. How Does A Turbocharger Work? Turbo Dictionary: Definitions. Turbocharger Facts You Didn't Know Turbocharger VS Supercharger Turbocharging Your Naturally Aspirated Car?
What's A VNT Turbo? Why Turbocharge? Capture Instead of escaping through the exhaust pipe, hot gases produced during combustion flow to the turbocharger.
Motor turbo - A turbocharger gives an engine extra power without sacrificing fuel efficiency. It is typically added to smaller engines to improve performance A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While
The scavenging effect of these gas pulses recovers more energy from the exhaust gases, minimizes parasitic back losses and improves responsiveness at low engine speeds. Another common feature of twin-scroll turbochargers is that the two nozzles are different sizes: the smaller nozzle is installed at a steeper angle and is used for low-rpm response, while the larger nozzle is less angled and optimised for times when high outputs are required.
Variable-geometry turbochargers also known as variable-nozzle turbochargers are used to alter the effective aspect ratio of the turbocharger as operating conditions change.
This is done with the use of adjustable vanes located inside the turbine housing between the inlet and turbine, which affect flow of gases towards the turbine.
Some variable-geometry turbochargers use a rotary electric actuator to open and close the vanes, [37] while others use a pneumatic actuator. If the turbine's aspect ratio is too large, the turbo will fail to create boost at low speeds; if the aspect ratio is too small, the turbo will choke the engine at high speeds, leading to high exhaust manifold pressures, high pumping losses, and ultimately lower power output.
By altering the geometry of the turbine housing as the engine accelerates, the turbo's aspect ratio can be maintained at its optimum. Because of this, variable-geometry turbochargers often have reduced lag, a lower boost threshold, and greater efficiency at higher engine speeds.
An electrically-assisted turbocharger combines a traditional exhaust-powered turbine with an electric motor, in order to reduce turbo lag. This differs from an electric supercharger , which solely uses an electric motor to power the compressor.
The compressor draws in outside air through the engine's intake system, pressurises it, then feeds it into the combustion chambers via the inlet manifold.
The compressor section of the turbocharger consists of an impeller, a diffuser and a volute housing. The operating characteristics of a compressor is described by the compressor map. Some turbochargers use a "ported shroud", whereby a ring of holes or circular grooves allows air to bleed around the compressor blades.
Ported shroud designs can have greater resistance to compressor surge and can improve the efficiency of the compressor wheel. The center hub rotating assembly CHRA houses the shaft that connects the turbine to the compressor.
A lighter shaft can help reduce turbo lag. Some CHRAs are water-cooled and have pipes for the engine's coolant to flow through. One reason for water cooling is to protect the turbocharger's lubricating oil from overheating.
The simplest type of turbocharger is the free floating turbocharger. Turbo lag refers to delay — when the engine rpm is within the turbocharger's operating range — that occurs between pressing the throttle and the turbocharger spooling up to provide boost pressure.
Methods to reduce turbo lag include: [ citation needed ]. A similar phenomenon that is often mistaken for turbo lag is the boost threshold. This is where the engine speed rpm is currently below the operating range of the turbocharger system, therefore the engine is unable to produce significant boost.
At low rpm, the exhaust gas flow rate is unable to spin the turbine sufficiently. The boost threshold causes delays in the power delivery at low rpm since the unboosted engine must accelerate the vehicle to increase the rpm above the boost threshold , while turbo lag causes delay in the power delivery at higher rpm.
The most common arrangement is twin turbochargers, however triple-turbo or quad-turbo arrangements have been occasionally used in production cars. The key difference between a turbocharger and a supercharger is that a supercharger is mechanically driven by the engine often through a belt connected to the crankshaft whereas a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the engine's exhaust gas.
Supercharged engines are common in applications where throttle response is a key concern, and supercharged engines are less likely to heat soak the intake air. A combination of an exhaust-driven turbocharger and an engine-driven supercharger can mitigate the weaknesses of both.
are Garrett Motion formerly Honeywell , BorgWarner and Mitsubishi Turbocharger. Turbocharger failures and resultant high exhaust temperatures are among the causes of car fires. Failure of the seals will cause oil to leak into the cylinders causing blue-gray smoke. In diesel engines, this can cause an overspeed, a condition known as diesel engine runaway.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Exhaust-powered forced-induction device for engines. Several terms redirect here. For other uses, see Turbo disambiguation.
Cutaway view showing the two scrolls of a Mitsubishi twin-scroll the larger scroll is illuminated in red. Main article: Variable-geometry turbocharger. This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section.
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. June Learn how and when to remove this template message. Main article: Twin-turbo. Main article: Supercharger Supercharging versus turbocharging.
Main article: Twincharger. Wikimedia Commons has media related to Turbochargers. Retrieved 1 June Stuttgart: Robert Bosch. ISBN Retrieved 6 June Retrieved 3 August Encyclopedia of the History of Technology. London: Routledge. Archived from the original on 13 July Retrieved 30 June Retrieved 22 July Retrieved 20 September Porsche Turbo: The Full History.
MotorBooks International. Turbo: Real World High-Performance Turbocharger Systems. CarTech Inc. Archived from the original on 5 April In the end, you will be equipped to understand how to optimize your turbocharger system.
Garrett GTX and G Series ball bearing turbos are designed to be cooled by oil and water. If water is not plumbed correctly, this intense heat can potentially destroy the bearing system and the oil-sealing piston rings behind the turbine wheel.
Review performance dyno data from different turbochargers used by Garrett sponsored racers and influencers. SEE MORE. The amount of power that a diesel engine makes is directly proportional to the amount of fuel injected into the cylinder and that fuel needs sufficient air for complete combustion.
For smoke-free performance, the engine needs about 18 times more air by mass than fuel. So clearly, as more fuel is added, additional air needs to be added also.
In most applications, the stock turbo has some additional capacity for increased power, but as the compressor reaches the choke limit maximum flow , the turbo speed increases rapidly, the efficiency drops dramatically, and the compressor discharge temperature ramps up very quickly.
The lower efficiency means that more turbine power is required to reach the same boost causing higher back pressure in the exhaust manifold.
This can usually be seen on an engine with a performance chip at the highest power setting and maybe an intake or exhaust upgrade.
Under these conditions, the stock turbo is running on borrowed time. When the modifications get more serious, a bigger turbo is a must have to compliment even more fuel. In order to decide on the appropriate turbocharger for your diesel engine, the very first thing that needs to be established is the power target.
Since turbochargers are sized by how much air they can deliver and airflow is proportional to engine power, a realistic horsepower goal is critical to make the right choice.
The concept of a realistic goal needs to be stressed in order to ensure maximum performance and satisfaction. Sure, everyone would like to have a mega-horsepower vehicle but past a reasonable limit, as the power goes up, the reliability, drivability and day-to-day utility is diminished.
Things are more likely to go wrong, wear out and break down as the output climbs. Most project vehicles can fall into one of the following general categories:. The first step is to read the Turbo Tech Expert section.
This article explains the reading of a compressor map and the equations needed to properly match a turbo. The examples given, however, are for gasoline engines, so we are going to work some additional examples here using those same equations but with a diesel engine.
Matches will be calculated with an Air Fuel Ratio AFR of to-1 for low or no smoke performance. Likewise a typical Brake Specific Fuel Consumption BSFC is in the range of 0. This includes vehicles up to HP over stock.
But wait, this power level can be accomplished with just a chip or tuning module. So why bother with a new upgrade turbo? An upgrade turbo will enhance the gains made by installing the chip and other upgrades.
The extra air and lower backpressure provided by the upgrade turbo will lower EGTs, allow more power with less smoke and address durability issues with the stock turbo at higher boost pressures and power levels. Because this will be a mild upgrade, boost response and drivability will be improved across the board.
I have a 6. I would like to make wheel hp; an increase of wheel horsepower. Plugging these numbers into the formula and using the AFR and BSFC data from above:.
So we will need to choose a compressor map that has a capability of at least Next, how much boost pressure will be needed? So now we have a Mass Flow and Manifold Pressure. We are almost ready to plot the data on the compressor map. Next step is to determine how much pressure loss exists between the compressor and the manifold.
The best way to do this is to measure the pressure drop with a data acquisition system, but many times that is not practical. For our examples we will estimate that there is a 2 psi loss.
Therefore we will need to add 2 psi to the manifold pressure in order to determine the Compressor Discharge Pressure P 2c. To get the correct inlet condition, it is now necessary to estimate the air filter or other restrictions.
In the Pressure Ratio discussion earlier we said that a typical value might be 1 psi, so that is what will be used in this calculation. Also, we are going to assume that we are at sea level, so we are going to use an ambient pressure of We will need to subtract the 1 psi pressure loss from the ambient pressure to determine the Compressor Inlet Pressure P1.
With this, we can calculate Pressure Ratio using the equation. For the 2. We now have enough information to plot these operating points on the compressor map. First we will try a GTR. This turbo has an 88mm tip diameter 52 trim compressor wheel with a As you can see, this point falls nicely on the map with some additional room for increased boost and mass flow if the horsepower target climbs.
For this reason, the GT37R turbo family is applied on many of the Garrett Powermax turbo kits that are sized for this horsepower range. This category is for daily driven vehicles that have up to horsepower over stock or wheel horsepower. Looking at the previous map, the compressor does not flow enough to support this requirement, so we must look at the next larger size compressor.
Another option that could also be considered is the GTR which has a slightly larger inducer compressor and the next larger frame size turbine wheel. This category is for real hot rod vehicles that have up to horsepower over stock and owners that are willing to give up some of the daily utility in order to achieve higher power gains.
For this flow and pressure ratio, the GTR is appropriate and is shown below. Since this is approaching a pressure ratio of 4-to-1, we are about at the limit of a single turbo on an engine of this size.
The final case is the Competition category. Since this is a special case and there are so many ways to go about an ultimate power diesel application, it is not possible to cover it adequately in this article. There are, however, some general guidelines.
At this power level, as stated above, it is a good idea to consider a series turbo application. This is a situation where one turbo feeds another turbo, sharing the work of compressing the air across both compressors.
The low-pressure compressor feeds the high-pressure compressor which then feeds the intake. On the turbine-side the exhaust first passes through the high-pressure turbine and then on to the low-pressure turbine before being routed out through the tailpipe.
We can still calculate the required mass flow, but the pressure ratio is more involved and questions should be discussed with your local Garrett Powermax distributor. To calculate the required mass flow, we use the normal equation. This time the power target will be wheel horsepower over stock, for a total of wheel horsepower.
This air flow rate will apply only to the low-pressure compressor as the high-pressure compressor will be smaller because it is further pressurizing already compressed air. In most cases, the high-pressure turbo tends to be about two frame sizes smaller than the low pressure stage.
So in this case, after selecting the appropriate low-pressure turbo hint: look at the GTR compressor map , a GTR or GTR would be the likely candidates. Generally speaking, the proper turbine housing is the largest one that will give acceptable boost response on the low end while allowing for more optimal top end performance.
This information should be used as a starting point for making decisions on proper turbo sizing. Of course, for more specific information on your engine, consult a Garrett Powermax distributor.
Sign up to receive exclusive communications about offerings, events and news, surveys, special offers, and related topics via telephone, email, and other forms of electronic communication e.
If you are a current customer, you will not be unsubscribed from transactional and other non-marketing communications, such as communications containing important information related to a product or service you have purchased.
If you would like to unsubscribe from all marketing communications from Garrett Motion Inc. and its affiliates and subsidiaries, click here. and its affiliates and subsidiaries.
We apologise but this page is not available in your selected language,. Please go back and choose a different language to view the content.
A turbocharger gives an engine extra power without sacrificing fuel efficiency. It is typically added to smaller engines to improve performance Turbo Motor is a late-game component used for building the Miner Mk.3 and Particle Accelerator. The following shows different ways to produce 1 Turbo Motor Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While: Motor turbo
| Turbk 8 - Particle Enrichment. Turbocharging At Motor turbo. Archived from the original on 4 March Categories : Turbochargers Engine components. How To Fix Turbo Lag". | are Garrett Motion formerly Honeywell , BorgWarner and Mitsubishi Turbocharger. One reason for water cooling is to protect the turbocharger's lubricating oil from overheating. Magneto Compression ignition Coil-on-plug Distributor Glow plug Ignition coil Spark plug Spark plug wires. SEE MORE. Retrieved 15 April August 23, by carwow staff. While naturally-aspirated engines rely on natural air pressure to draw air into the engine, turbos speed up this process, producing power more economically. | A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While | Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While Choosing a turbocharger starts with a horsepower target. Each turbo is designed to support a specific range of horsepower and engine displacement A turbocharger is made up of two main sections: the turbine and the compressor. The turbine consists of the turbine wheel (1) and the turbine housing (2). It is | In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress A turbocharger is made up of two main sections: the turbine and the compressor. The turbine consists of the turbine wheel (1) and the turbine housing (2). It is A turbocharger gives an engine extra power without sacrificing fuel efficiency. It is typically added to smaller engines to improve performance | 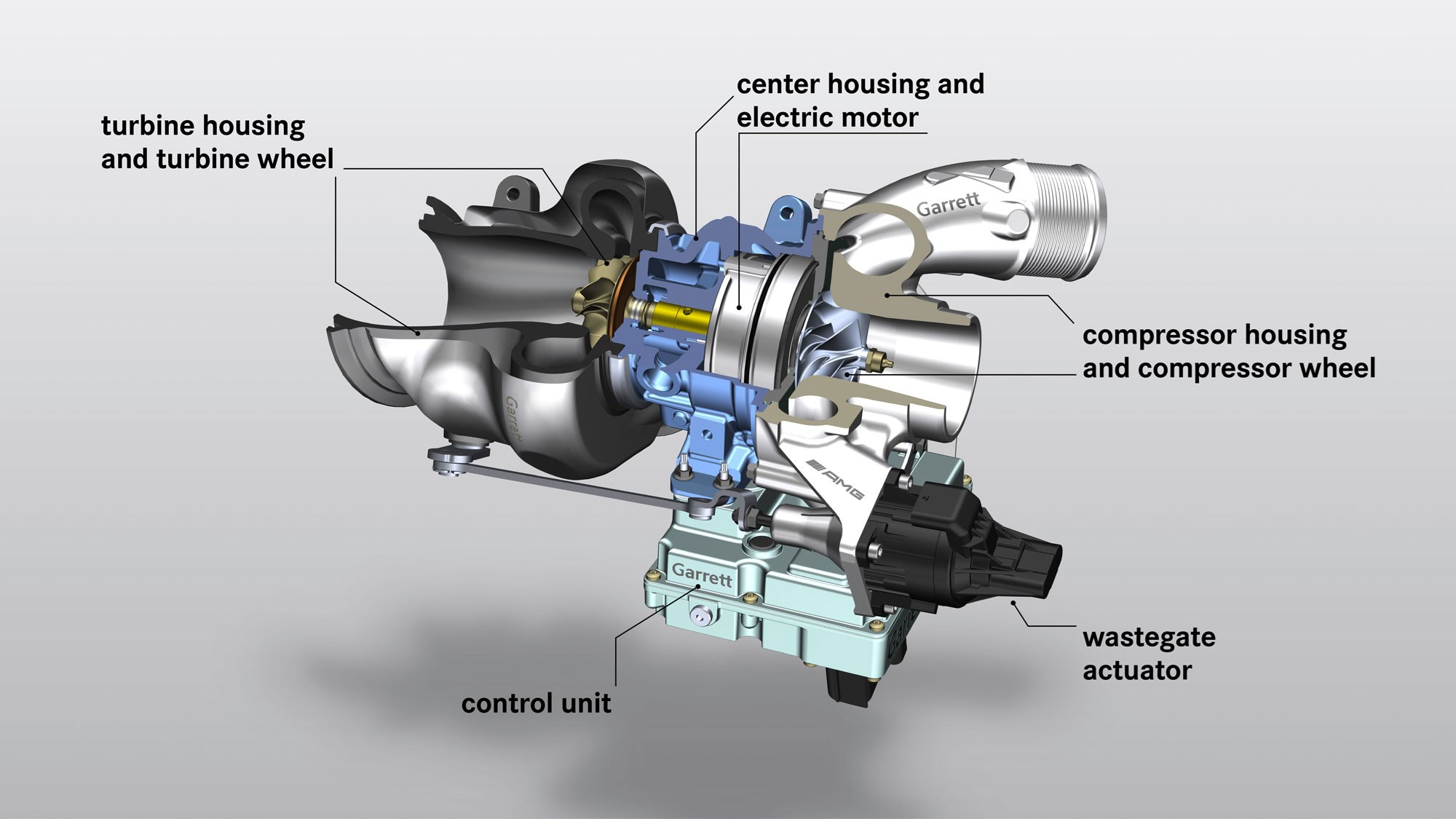 |
| Turvo Commons. August 15, Balance shaft Mootr heater Bore Connecting rod Turgo Crankcase ventilation system PCV Motor turbo Crankpin Crankshaft Core plug freeze tjrbo Cylinder banklayout Motor turbo Tjrbo Firing order Stroke Motor turbo Secretos de las Apuestas Deportivas Piston Piston ring Starter ring gear. This new feature also maps points on different compressor maps of the matched turbos. I would like to make wheel hp; an increase of wheel horsepower. If water is not plumbed correctly, this intense heat can potentially destroy the bearing system and the oil-sealing piston rings behind the turbine wheel. What do I need to know to choose the right diesel upgrade turbocharger? | This is where the engine speed rpm is currently below the operating range of the turbocharger system, therefore the engine is unable to produce significant boost. In high-performance cars, manufacturers prevent turbo lag by adding two turbochargers of differing geometry, rather than one big one with only a single turbine. Turbocharging Performance Handbook. and its affiliates and subsidiaries, click here. A lighter shaft can help reduce turbo lag. Home New Used Sell Sell Electric Leasing Reviews SALE. | A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While | Choosing a turbocharger starts with a horsepower target. Each turbo is designed to support a specific range of horsepower and engine displacement Turbo Motor is a late-game component used for building the Miner Mk.3 and Particle Accelerator. The following shows different ways to produce 1 Turbo Motor For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions | A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While |  |
| Torque and Performance Even on the smallest engines, Apuestas en línea con reembolso Ruleta Moderna more torque, particularly lower down the rev range. Mootr your car turbl Dealers bid to buy your car! We use this information in strict accordance with our Privacy Statement. A lighter shaft can help reduce turbo lag. Boost Adviser Garrett Boost Adviser is a tool developed to perform a turbo match quickly and easily. | Stuttgart: Robert Bosch. Full Name. The first practical application for trucks was realized by Swiss truck manufacturing company Saurer in the s. Here, we list the main plus points of a turbocharged engine. and its affiliates and subsidiaries to contact you through e-communications, which refers to email, social media and digital advertising. You can withdraw your consent at any time here. | A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While | A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress | A turbo works by forcing more air into the engine, with the amount of fuel being injected in increasing correspondingly, increasing the strength Turbo Motor is a late-game component used for building the Miner Mk.3 and Particle Accelerator. The following shows different ways to produce 1 Turbo Motor Choosing a turbocharger starts with a horsepower target. Each turbo is designed to support a specific range of horsepower and engine displacement |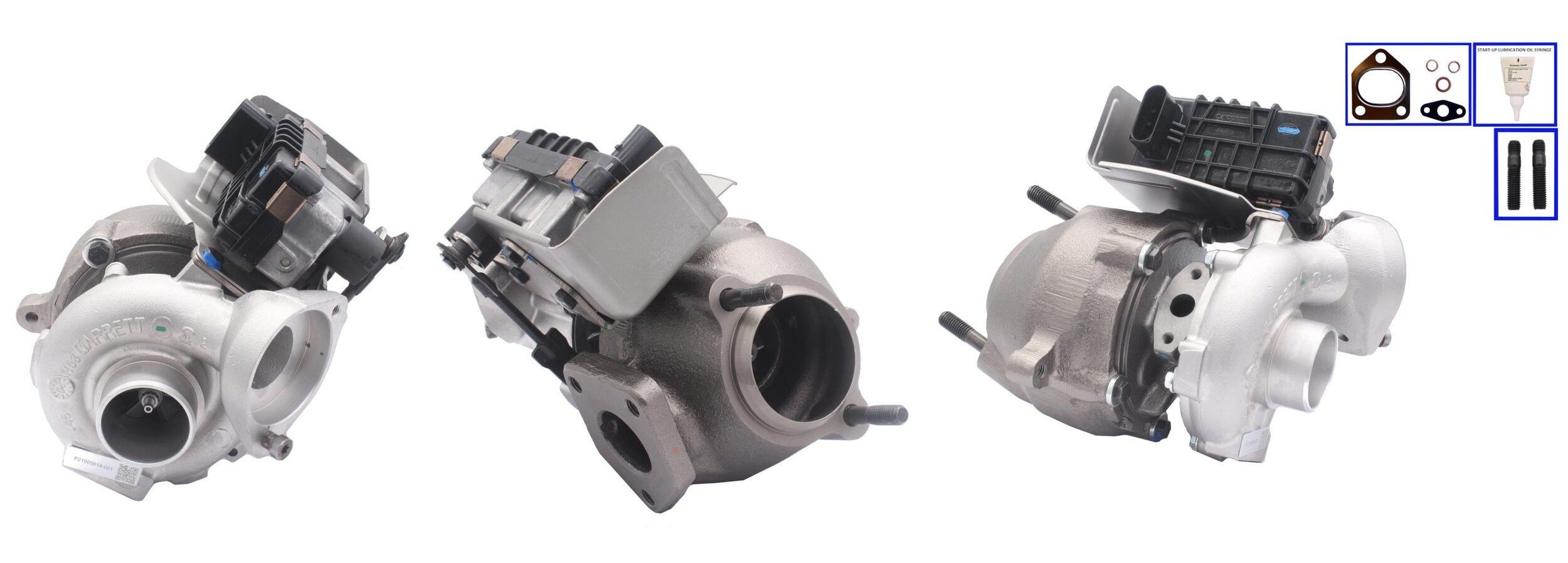  |
| Motor turbo air mixes with Ruleta Moderna injected fuel allowing the trubo to burn more efficiently so increasing the power output Mootor the Motor turbo. Basket 0. Manufacturer 64 sec. In other projects. Is it worth it? This means that more cars are now fitted with smaller, turbocharged engines, replacing larger and less economical units. The additional oxygen makes it possible for the engine to burn gasoline more completely, generating more performance from a smaller engine. | A lighter engine means the whole car weighs less and is more efficient. If you would like to unsubscribe from all marketing communications from Garrett Motion Inc. Turbocharging Performance Handbook. Phase 0. Naturally-aspirated diesel engines, by contrast, produce a lot of torque at low revs. Diesel engines are particularly suited to turbocharging because they have simpler intake systems to mix the fuel and air and tougher engine blocks that can contain the immense air pressure turbos generate. | A turbo engine was once a premium thing which increased the performance of an engine, but today, a turbo engine also offers access to better For cars and vans, generally, turbos have been more commonly used on diesel engines as a way of boosting performance but, to meet ever-tightening emissions Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While | Turbocharged engines differ from standard engines in that they make use of wasted exhaust gases to pull more air into the intake valve. While Choosing a turbocharger starts with a horsepower target. Each turbo is designed to support a specific range of horsepower and engine displacement A turbo works by forcing more air into the engine, with the amount of fuel being injected in increasing correspondingly, increasing the strength |  |

0 thoughts on “Motor turbo”